# 数据类型
# 数据类型
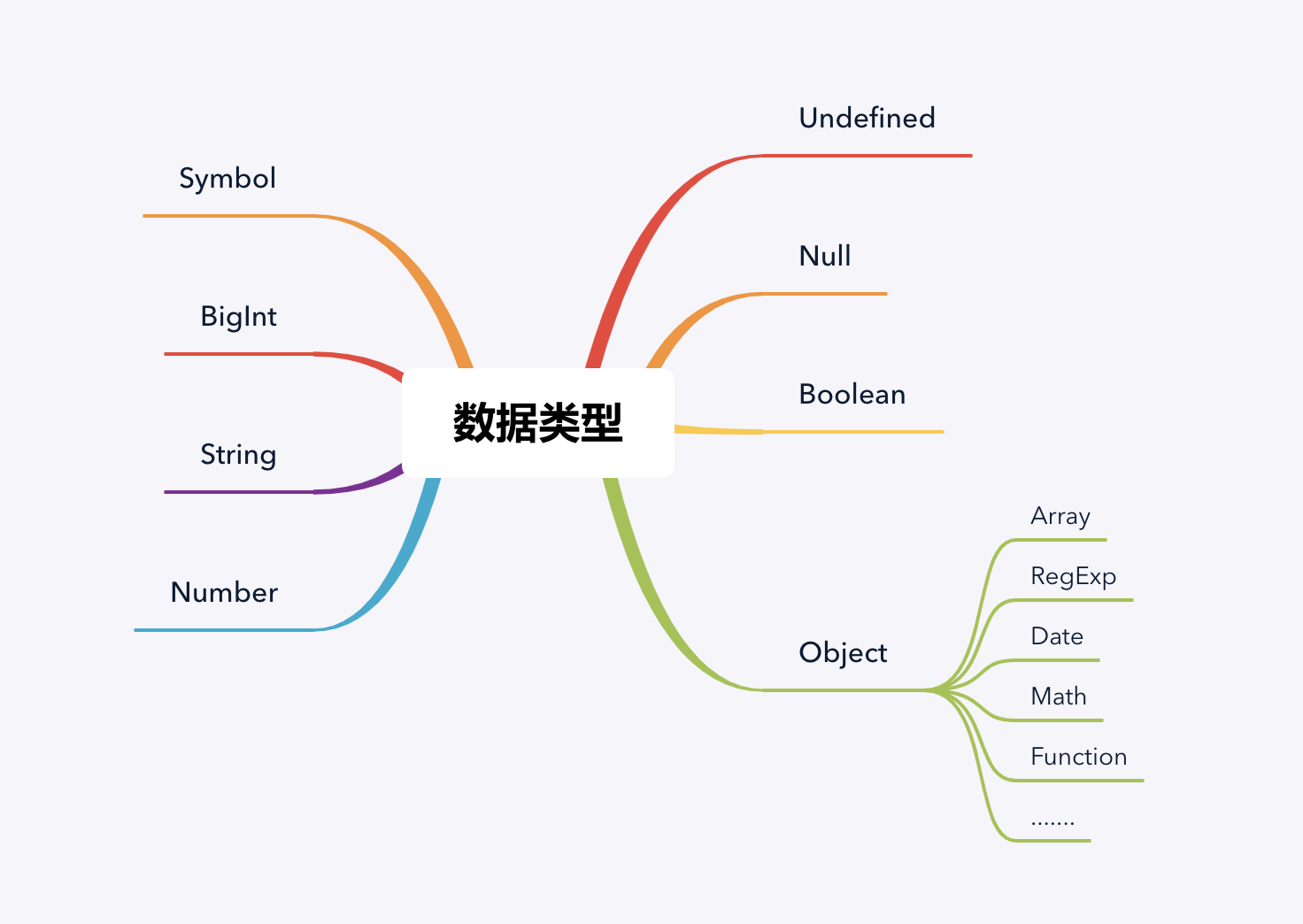
基础类型有七种,分别为
Number,String,Boolean,Null,Undefined,Symbol,BigInt。其中Symbol,BigInt都是es6之后新出的类型。后面Symbol、BigInt章节会具体讲一下是什么,且常见什么使用场景。复杂类型:
Object。其中js中内置了一些复杂类型的对象。例如Date,Math,RegExp,Function,Array等等。
# 检测数据类型
# typeof
用来区分基础类型和复杂类型,基础类型能够得到自己的类型,复杂类型得到object。注意null 和 函数 的检测会比较特殊,typeof null得到object,typeof 函数得到function。
typeof(1); // number
typeof('c'); // string
typeof(false); // boolean
typeof(undefined); // undefined
typeof(Symbol('a symbol')); // symbol
typeof(1n); // bigint
typeof({}); // object
// 特殊 函数 和 null
typeof(() => {}); // function
typeof(null); // object
另外如果typeof [某个没有声明的变量]会得到 undefined,这个特性有什么用呢,这帮助我们在程序中检查变量 有没有声明 ,但却不会出现 ReferenceError: xx is not defined 错误,或者某个全局api存不存在,做一些polyfill,这些场景 typeof 的 安全防范机制就成了我们的好帮手:
typeof bowlofnoodles; // undefined => 检测有没有声明这个变量
if (typeof atob === 'undefined') { // => 检测某个全局api有没有
atob = function() { /*..*/ };
}
# instanceof
采用 MDN 的说法就是,instanceof 运算符用于检测构造函数的 prototype 属性是否出现在某个实例对象的原型链上。
function Car(make, model, year) {
this.make = make;
this.model = model;
this.year = year;
}
const auto = new Car('Honda', 'Accord', 1998);
auto instanceof Car; // true
auto instanceof Object; // true Object.prototype也在auto的原型链上
const car = new String('bowlofnoodles')
car instanceof String // true
const str = 'bowlofnoodles'
str instanceof String // false 这里也比较特殊 普通类型
# Array.isArray
特定用于数组,检测一个变量是不是数组类型。
const arr = [1, 2, 3];
const obj = {};
Array.isArray(arr); // true
Array.isArray(obj); // false
# Object.prototype.toString.call
Object.prototype.toString.call的方式是最全的检测方法,调用Object原型上的toString方法得到类似 "object [类型]"的字符串,注意类型的首字母是大写。例如Date类型得到"object Date"。
Object.prototype.toString({}) // "[object Object]"
Object.prototype.toString.call({}) // 同上结果,加上call也ok
Object.prototype.toString.call(1) // "[object Number]"
Object.prototype.toString.call('1') // "[object String]"
Object.prototype.toString.call(true) // "[object Boolean]"
Object.prototype.toString.call(Symbol()) // "[object Symbol]"
Object.prototype.toString.call(1n) // "[object BigInt]"
Object.prototype.toString.call(function(){}) // "[object Function]"
Object.prototype.toString.call(null) //"[object Null]"
Object.prototype.toString.call(undefined) //"[object Undefined]"
Object.prototype.toString.call(/123/g) //"[object RegExp]"
Object.prototype.toString.call(new Date()) //"[object Date]"
Object.prototype.toString.call([]) //"[object Array]"
Object.prototype.toString.call(document) //"[object HTMLDocument]"
Object.prototype.toString.call(window) //"[object Window]"
Object.prototype.toString.call(Math) //"[object Math]"
两个小问题,有时候会被问到:
为什么不直接调用
Object.prototype.toString而要调用call方法,因为这样调用是求Object.prototype这个对象toString的值这样一定都是"object Object"结果。既然是
Object.prototype上实现的方法,为什么不直接实例调用,根据原型链也可以访问的到,例如[1, 2, 3].toString。原因是有些类型会自己实现一个toString方法,根据原型链访问属性一层一层往上追溯原则,Object.prototype上的toString方法会被屏蔽掉。例如[1, 2, 3].toString会得到1,2,3的结果,原因就是Array.prototype上的toString方法实现。
const num = 1;
const arr = [1, 2, 3];
num.toString(); // '1'
arr.toString(); // '1,2,3'